Most overlook this. 12 critical signs of vitamin B12 deficiency and what to do
McKayla Davis
Contributing Writer
Vitamin B12 deficiency is a common yet often overlooked health issue that can lead to a range of debilitating symptoms. Despite its importance, many people are unaware of the signs and the potential long-term consequences of not addressing this deficiency. Vitamin B12 is crucial for the production of red blood cells and the maintenance of a healthy nervous system. A deficiency can result from various factors, including dietary choices, medical conditions, and certain medications. Understanding and recognizing the signs of vitamin B12 deficiency is essential for maintaining optimal health.
Understanding the Importance of Vitamin B12
Vitamin B12, also known as cobalamin, is a water-soluble vitamin that plays a vital role in brain function and the production of DNA and red blood cells. It is essential for the proper functioning of the nervous system and the formation of blood. Unlike other vitamins, B12 is not produced by the body and must be obtained through diet or supplements. It is primarily found in animal products, which means vegetarians and vegans are at a higher risk of deficiency. Adequate levels of vitamin B12 are crucial for preventing anemia, supporting mental health, and ensuring overall well-being.
Common Causes of Vitamin B12 Deficiency
Several factors can contribute to vitamin B12 deficiency. Dietary insufficiency is a primary cause, particularly in individuals who follow a vegetarian or vegan diet without adequate supplementation. Malabsorption issues, such as those caused by pernicious anemia, celiac disease, or Crohn’s disease, can also lead to deficiency. Additionally, certain medications, including proton pump inhibitors and metformin, can interfere with B12 absorption. Age is another factor, as older adults are more prone to deficiency due to decreased stomach acid production, which is necessary for B12 absorption.
12 Critical Signs of Vitamin B12 Deficiency
Vitamin B12 deficiency can manifest in various ways, often mimicking other health conditions. Recognizing these signs early can prevent more severe health issues. Here are 12 critical signs to watch for:
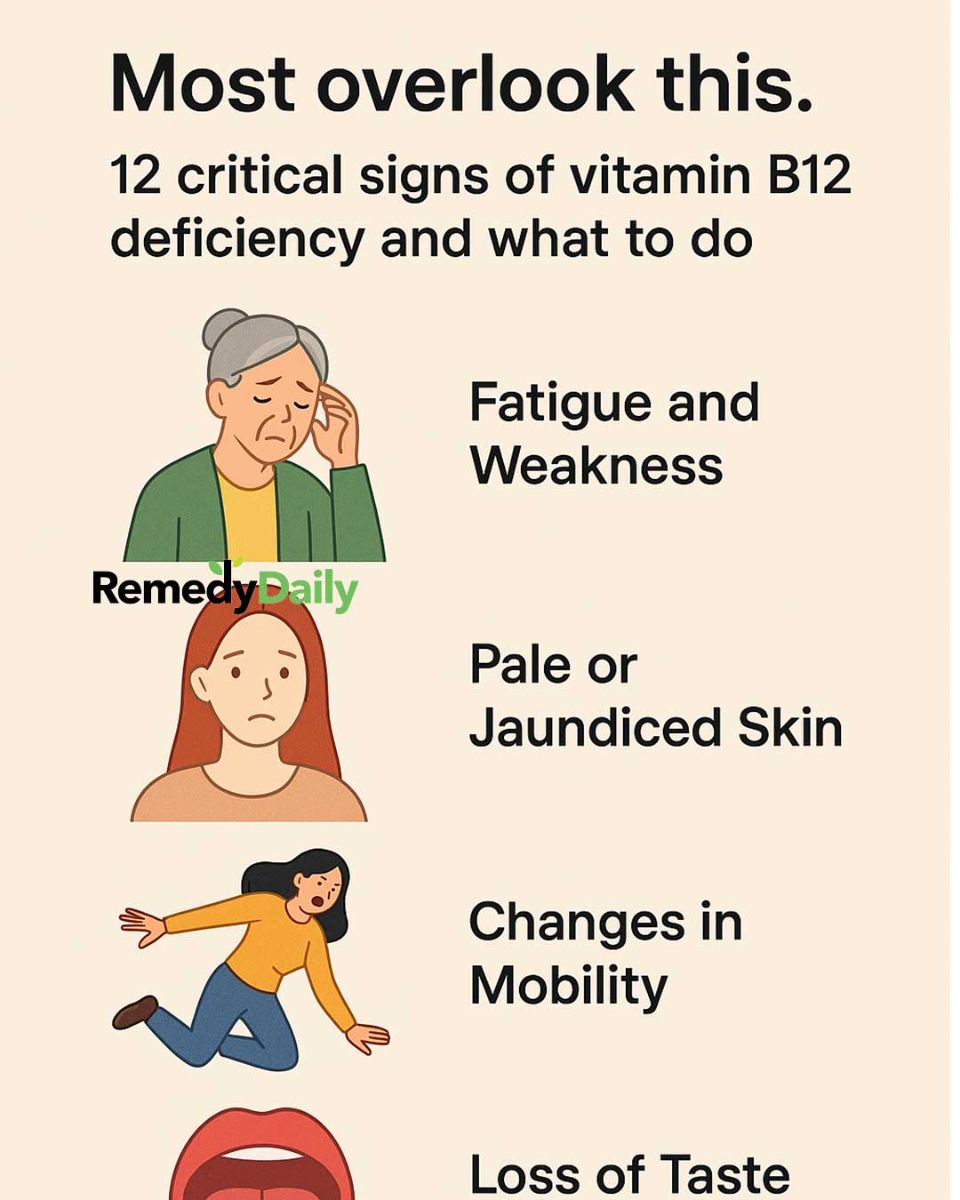
1. Fatigue and Weakness
One of the most common signs of vitamin B12 deficiency is persistent fatigue and weakness. This occurs because B12 is essential for red blood cell production, which carries oxygen throughout the body. Without enough oxygen, individuals may feel constantly tired and weak, even after a full night’s sleep.
2. Pale or Jaundiced Skin
A lack of vitamin B12 can lead to anemia, which often results in pale or yellow-tinged skin. This is due to the reduced production of red blood cells and the breakdown of existing ones, releasing bilirubin and causing a jaundiced appearance.
3. Nerve Problems Like Tingling or Numbness
Vitamin B12 is crucial for maintaining a healthy nervous system. A deficiency can lead to nerve damage, resulting in symptoms such as tingling, numbness, or a ‘pins and needles’ sensation in the hands and feet. This is due to the deterioration of the protective myelin sheath around nerves.
4. Changes to Mobility
As nerve damage progresses, it can affect balance and coordination, leading to changes in mobility. Individuals may experience difficulty walking, frequent stumbling, or a general lack of coordination, which can increase the risk of falls and injuries.
5. Glossitis and Mouth Ulcers
Glossitis, or inflammation of the tongue, can be an early sign of vitamin B12 deficiency. The tongue may appear swollen, red, and smooth, often accompanied by pain. Mouth ulcers may also develop, causing additional discomfort.
6. Breathlessness and Dizziness
Due to reduced red blood cell production, individuals with B12 deficiency may experience breathlessness and dizziness, especially during physical activity. This is because the body struggles to deliver enough oxygen to tissues and organs.
7. Disturbed Vision
In severe cases, vitamin B12 deficiency can damage the optic nerve, leading to blurred or disturbed vision. This condition, known as optic neuropathy, can result in vision loss if not addressed promptly.
8. Mood Changes
Vitamin B12 plays a role in the production of neurotransmitters that regulate mood. Deficiency can lead to mood changes, including depression, anxiety, and irritability. Some individuals may also experience cognitive difficulties, such as memory loss or confusion.
9. High Temperature
Although less common, some individuals with vitamin B12 deficiency may experience a slightly elevated body temperature. The exact cause is unclear, but it may be related to the body’s response to reduced red blood cell production.
10. Cognitive Impairment
Cognitive impairment, including memory loss and difficulty concentrating, can occur with vitamin B12 deficiency. This is due to the vitamin’s role in maintaining healthy brain function and the production of neurotransmitters.
11. Heart Palpitations